Straight Bar vs. EZ Bar Curls: Which Builds Bigger Biceps?
When most people think “arm day,” they think curls. But there’s one question that always comes up:
Should you use a straight bar or an EZ bar?
Both look similar — you’re curling a barbell to grow your biceps — but the small difference in the bar’s shape actually changes how your muscles work. Let’s break it down in plain language so you can train smarter.
What’s the Difference?
Straight Bar Curl
The straight bar keeps your hands fully palm-up (supinated).
This puts your biceps brachii — the main biceps muscle — in its strongest position.
It also puts more twist on your wrists and elbows, which can cause pain for some lifters.
EZ Bar Curl
The EZ bar is bent in the middle, so your hands sit at a slight angle instead of fully palm-up.
This is easier on your wrists and elbows.
It still works your biceps hard, but it also hits other muscles like the brachialis and brachioradialis, which help make your arms look thicker overall.
What Studies Say
Several studies have compared straight bar and EZ bar curls using EMG (which measures muscle activation).
🧠 Study #1 —
Marcolin et al., 2018
Researchers compared straight bar, EZ bar, and dumbbell curls.
They found:
Both bars activated the biceps about the same.
The EZ bar also hit the forearm muscles a bit more.
The biggest difference? Comfort — the EZ bar felt better for most people.
🧠 Study #2 —
Coratella et al., 2023
This newer study found that:
The straight bar gave the biceps slightly higher activation (only about 2–4% more).
The difference was so small that it probably doesn’t matter for most lifters.
The EZ bar was easier on the joints.
Bottom line from both studies:
👉 You can grow big biceps with either bar.
Which One Builds Bigger Biceps?
Here’s the truth:
Muscle growth comes down to consistency, volume, and effort — not which bar you use.
That said:
The straight bar might give a tiny edge for isolating your biceps.
The EZ bar is more joint-friendly, so you can often lift heavier or do more reps without pain.
If you can train harder and more often with the EZ bar, you’ll probably see better results overall — even if it’s technically 2% less biceps activation.
When to Use Each One
Example Workout
Biceps Growth Routine (Beginner Friendly):
- Straight Bar Curl – 4 sets of 8–10 reps
- EZ Bar Curl – 3 sets of 10–12 reps
- Hammer Curl (dumbbells) – 3 sets of 12–15 reps
Keep your elbows tight, control each rep, and focus on squeezing your biceps at the top.
The Takeaway
Both bars will build your biceps.
- Straight bar = slightly more pure biceps work.
- EZ bar = easier on your joints and better for long-term progress.
- The best choice? Whichever one helps you lift pain-free and push hard.
Pair that training with solid recovery and good nutrition (your Post ISO protein shake after workouts, for example), and your arms will grow — no matter which bar you pick.
Featured product











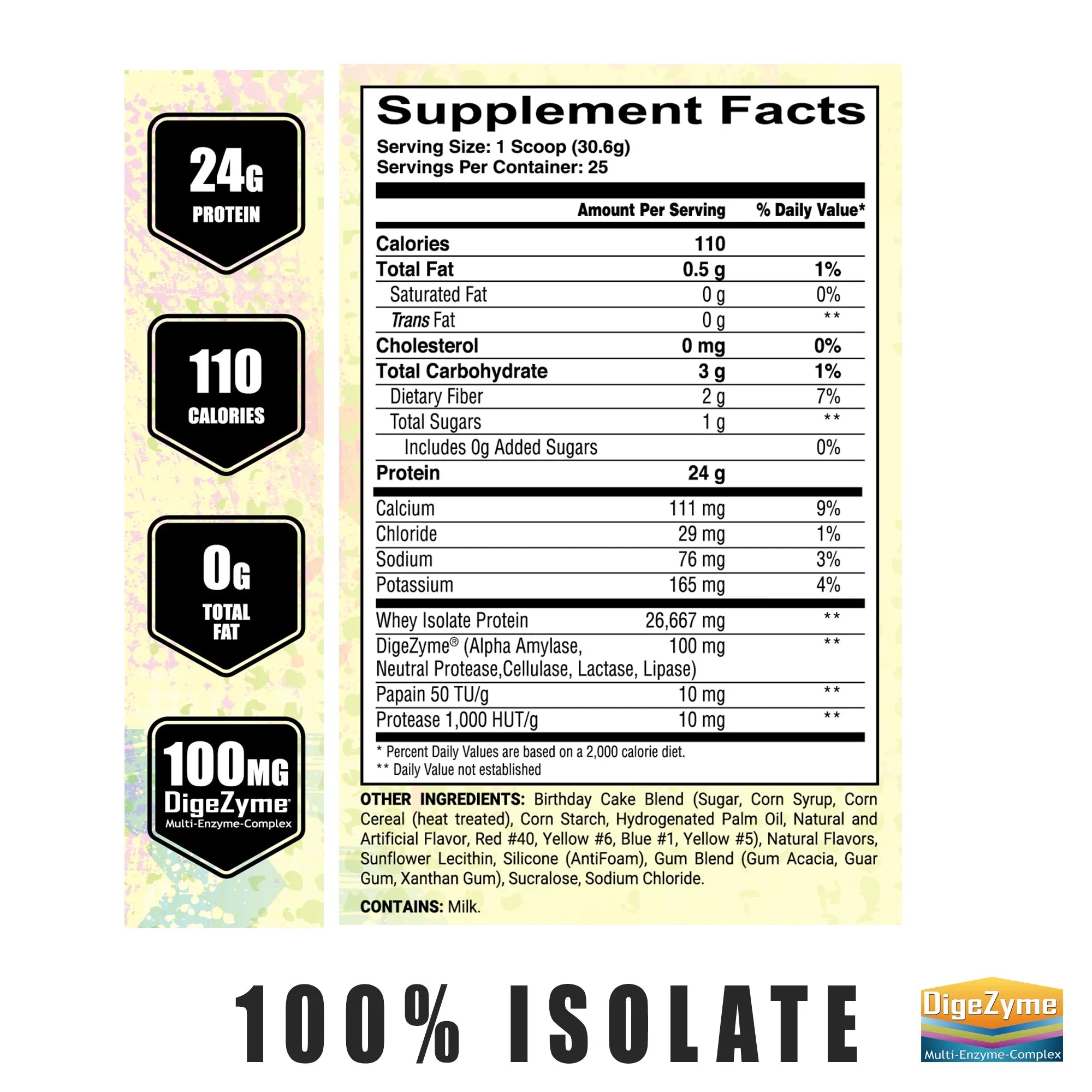


Amazing tasting protein powder
Pickup available at 11880 W. President Dr. Suite D
Usually ready in 24 hours

Post Iso
BLUEBERRY COBBLER
11880 W. President Dr. Suite D
11880 W President Dr
Suite D
Boise ID 83713
United States
The essentials
Share details of your store's product selection, or share a story that speaks to your customers.
Read more

In the pursuit of a healthier lifestyle, many of us have become increasingly conscious of our dietary choices. The rise of superfoods and health supplements has opened up new possibilities for enh...

When it comes to achieving fitness goals, protein intake plays a crucial role. Whether you're a dedicated athlete or simply aiming to live a healthier lifestyle, consuming an adequate amount of p...











